
Venezuela Votes to Annex 61,600 square miles Oil-Rich Essequibo Region from Guyana
Venezuela Votes to Annex 61 600 square miles Oil-Rich Essequi….. The longstanding territorial dispute between Venezuela and Guyana over the Essequibo region has escalated in recent years, culminating in a Venezuelan referendum asserting sovereignty over the area. This development raises critical questions about the potential for Venezuela to annex this part of Guyana and the broader implications for regional stability.
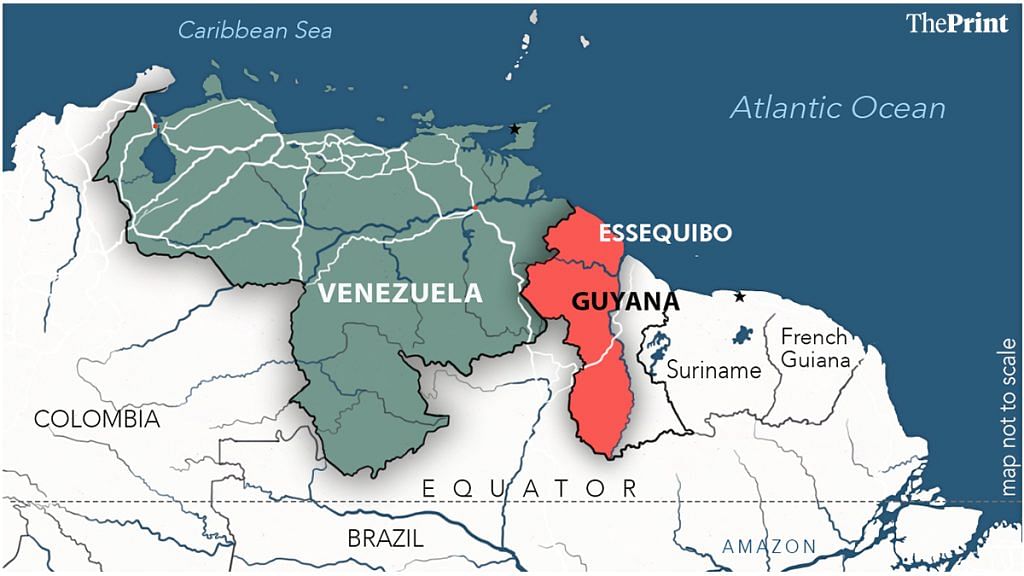
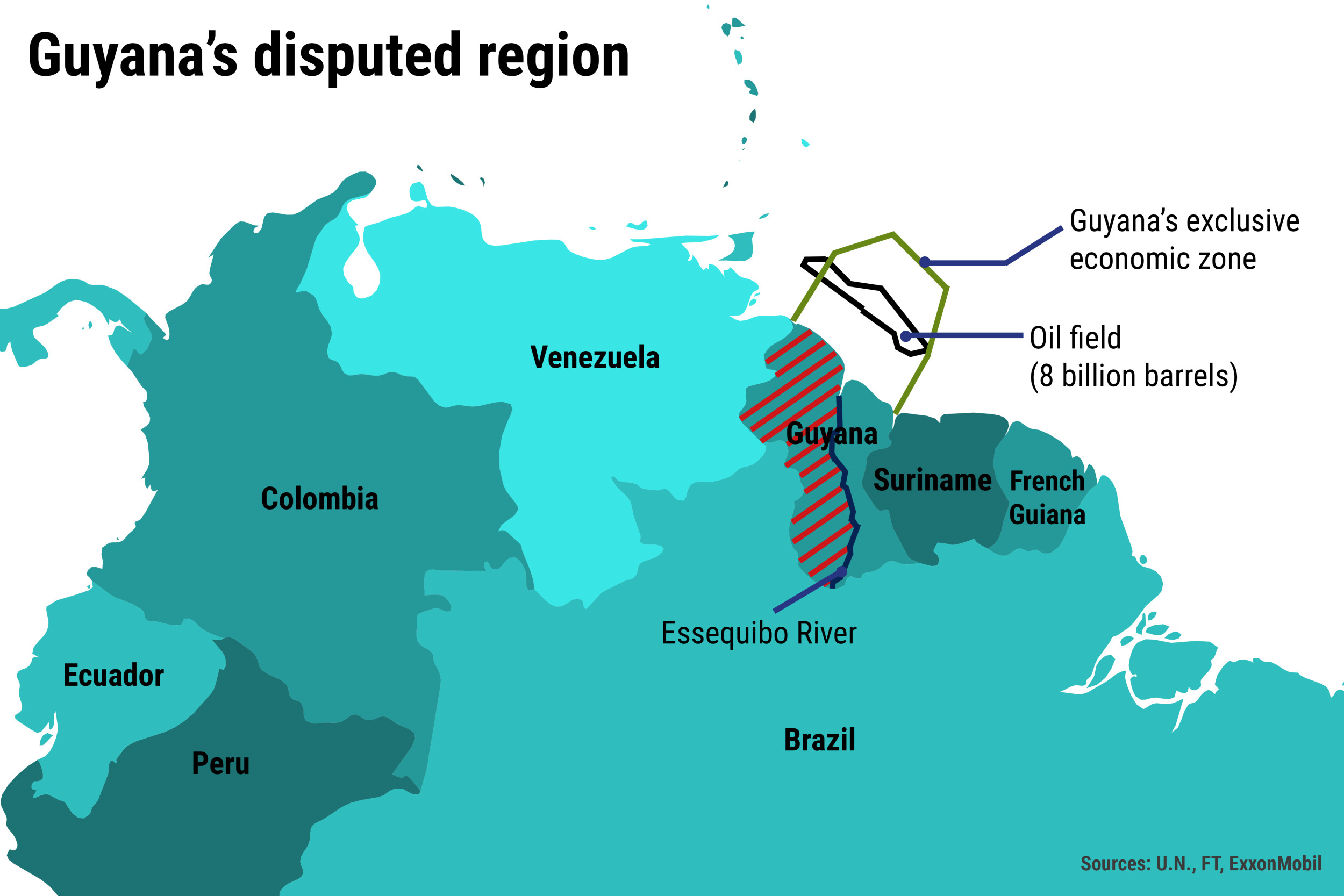
Historical Context of the Dispute
The Essequibo region, encompassing approximately 159,500 square kilometers west of the Essequibo River, has been a contentious area between Venezuela and Guyana for over a century. The current border was established by the 1899 Paris Arbitral Award, which granted the majority of the disputed territory to British Guiana, now Guyana. Venezuela accepted this decision initially but later contested it in 1962, alleging unfair arbitration practices. The dispute has persisted, with both nations maintaining claims over the territory.
Venezuelan Referendum and Its Implications
In December 2023, Venezuela conducted a referendum in which voters approved a government proposal to claim sovereignty over the Essequibo region. The National Electoral Council reported that over 10.5 million voters participated, reflecting significant domestic support for the government’s stance. President Nicolás Maduro’s administration argued that the referendum aimed to reaffirm Venezuela’s historical claim to the territory.
The international community, including organizations like the International Court of Justice (ICJ), has expressed concerns over Venezuela’s actions, cautioning against any attempts at annexation and urging adherence to peaceful and lawful resolution mechanisms.
Guyana’s Response and International Support
In reaction to Venezuela’s referendum and subsequent actions, Guyana has sought assistance from international bodies to uphold its territorial integrity. The Guyanese government approached the ICJ to prevent Venezuela from electing officials to govern the Essequibo region, viewing such moves as violations of international law and previous agreements to avoid escalating the conflict.
The United States and the Organization of American States have expressed support for Guyana, condemning Venezuela’s aggressive maneuvers and emphasizing the importance of respecting international boundaries and legal processes.
Recent Escalations and Military Tensions
Tensions have further escalated with incidents such as the construction of a bridge by Venezuelan armed forces on a disputed island in the Essequibo region, prompting formal protests from Guyana. Additionally, the incursion of a Venezuelan naval vessel into Guyanese waters near an ExxonMobil-operated oil facility led President Irfaan Ali to initiate a military response and seek international diplomatic support.
Economic Stakes: Oil and Mineral Resources
The Essequibo region is rich in natural resources, including significant oil reserves discovered offshore. Since 2015, companies like ExxonMobil have identified approximately 11 billion barrels of oil in Guyana’s waters, transforming the nation’s economy and attracting global business interest. This newfound wealth has intensified the territorial dispute, as control over the region implies substantial economic benefits
Legal Perspectives and International Mediation
The legal status of the Essequibo region is anchored in the 1899 arbitration award, which is recognized internationally as the legitimate demarcation of the boundary. Guyana’s recourse to the ICJ seeks to reaffirm this position and resolve the dispute through legal channels. The international community emphasizes the importance of upholding existing legal frameworks to prevent the dispute from escalating into armed conflict.
Potential for Annexation: Analyzing the Risks
While Venezuela’s referendum indicates strong domestic support for claiming the Essequibo region, actual annexation would require overcoming significant legal, diplomatic, and potentially military challenges. International law, as upheld by bodies like the ICJ, does not recognize unilateral annexation, especially when it contradicts established treaties and arbitration awards. Moreover, any aggressive moves by Venezuela could lead to regional instability and draw condemnation or intervention from other nations and international organizations.
Conclusion
The Venezuelan referendum to claim sovereignty over the Essequibo region represents a significant escalation in a long-standing territorial dispute with Guyana. While the referendum reflects domestic support within Venezuela, actual annexation faces substantial legal and diplomatic obstacles. The international community’s emphasis on peaceful resolution and adherence to legal processes is crucial in preventing the dispute from devolving into conflict and ensuring stability in the region.
Leave a Reply